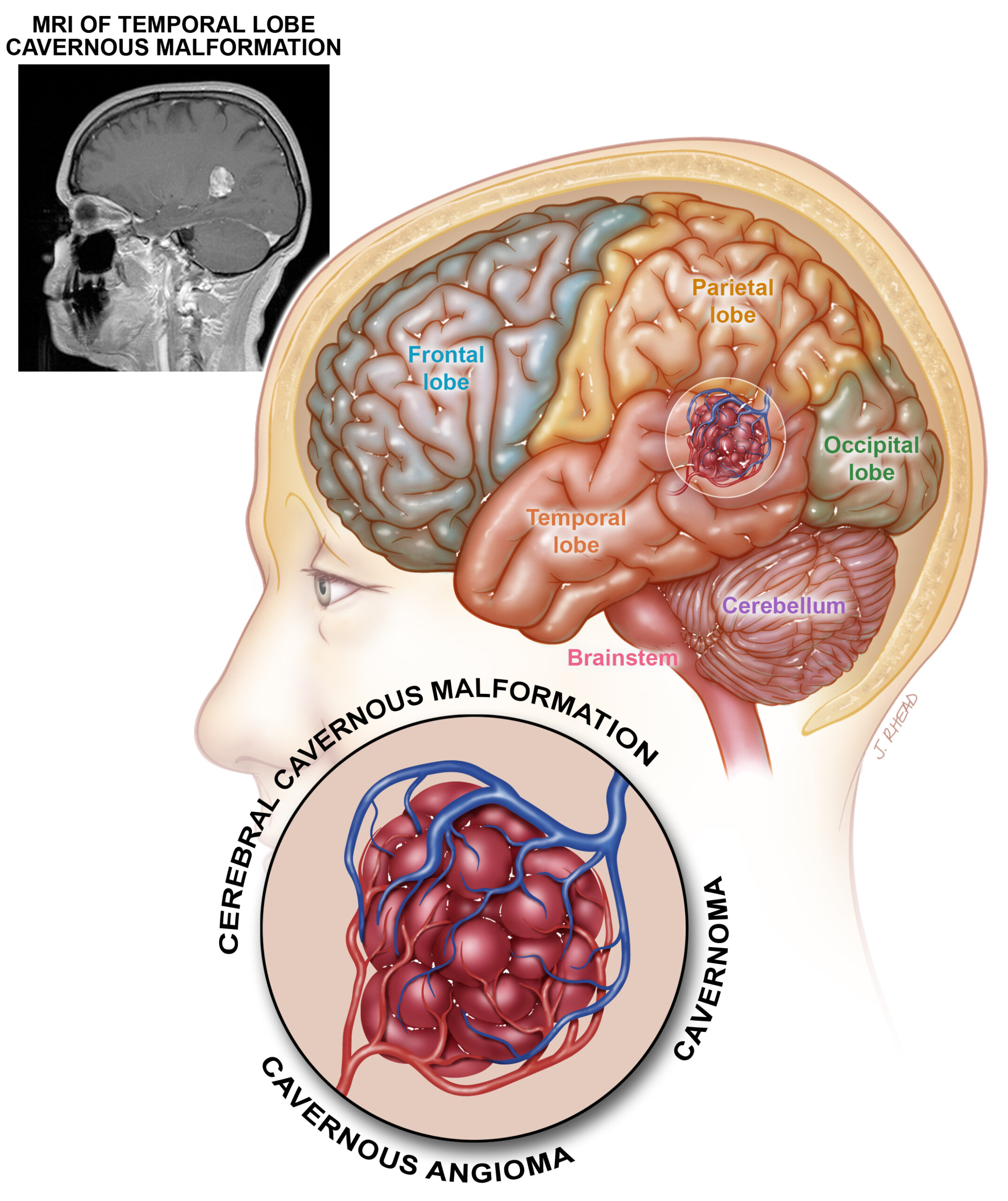
1) Cerebral Cavernous Malformation (CCM) is also known as cavernous angioma or cavernoma. Cavernoma is the term used most frequently outside of the United States. Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) is the term used in the research literature and in medical diagnosis.
2) A cavernous malformation is a mulberry-shaped abnormal blood vessel with thin, leaky walls.
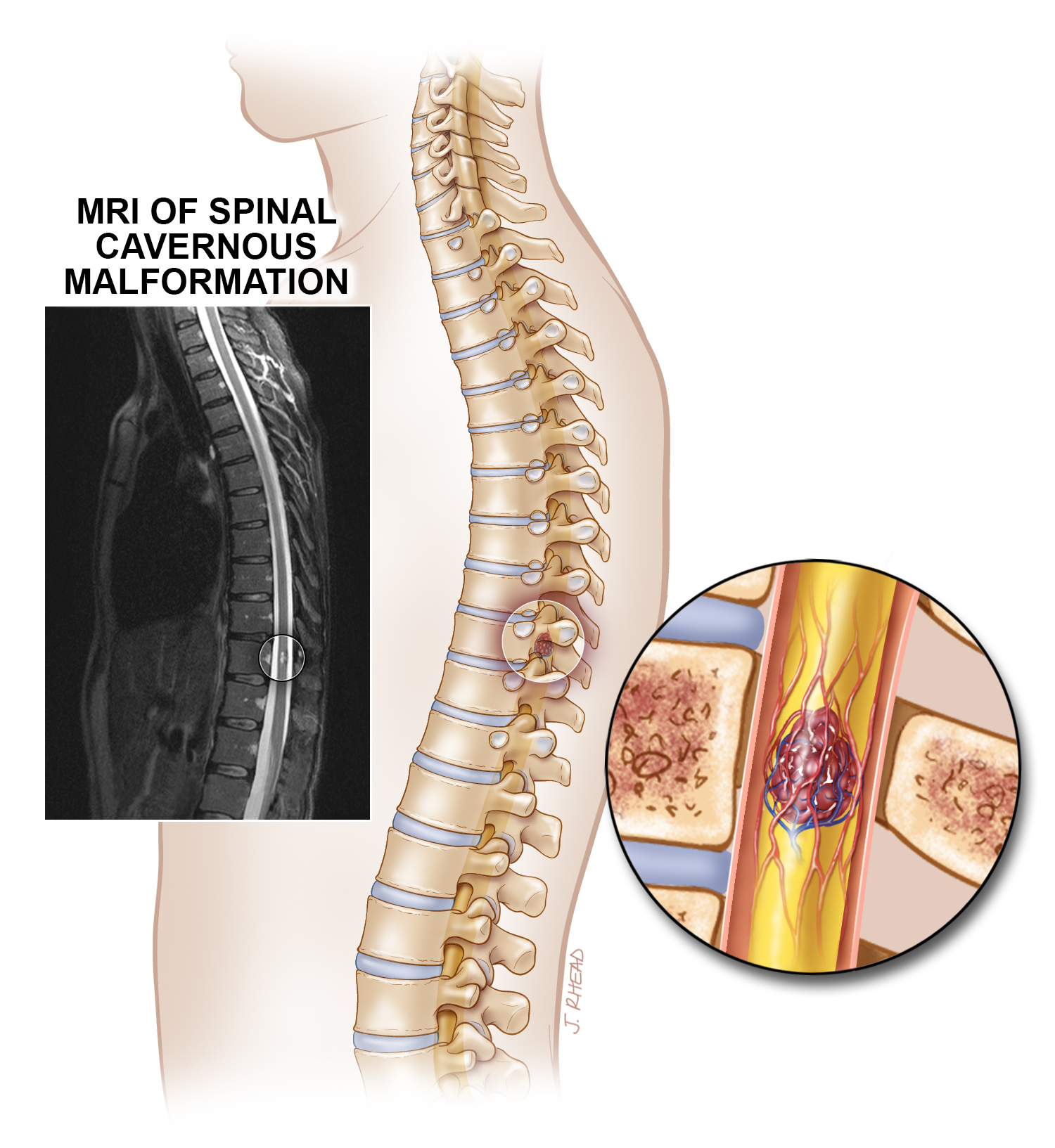
3) Cavernous malformations are found mostly in the brain and spinal cord.
4) 1 in 500 people have at least one cavernous malformation in their brain. Most people will have no symptoms.
5) Cavernous malformations can grow and hemorrhage at any age, including in young children. They are most likely to become symptomatic when a person is between the ages of 20-40.
6) The most common first symptom is seizure (50%), followed by hemorrhage (25%) and neurological deficits (25%) like blurred vision and weakness in limbs.
7) Cavernous malformation is hereditary in about 20% of people who have the illness.
8) Those with the hereditary form of the illness will have more than one cavernous malformation and will develop more lesions over time.
9) The hereditary form of the illness does not skip generations. Each child of an affected person has a 50/50 chance of inheriting the illness.
10) The hereditary form of the illness can be caused by a mutation on any one of three genes: CCM1, CCM2, and CCM3.
11) The hereditary form of the illness can happen in any family. However, there are several groups of people that are at higher risk for the hereditary form: descendants of the original Hispanic population of New Mexico where the mutation began in the mid-1600’s, the Ashkenazi Jewish population, and a European-American group with roots in the Southern states of the US.
12) Brain or spinal surgery is the only current treatment for the illness, but there are a number of medications under development to strengthen the vessels and stop more cavernous malformations (cavernomas) from forming.
Cavernous Malformation Fast Facts [PDF] to download for printing.
Updated 4.15.22

